What Are the Four Common Causes of Kidney Damage?
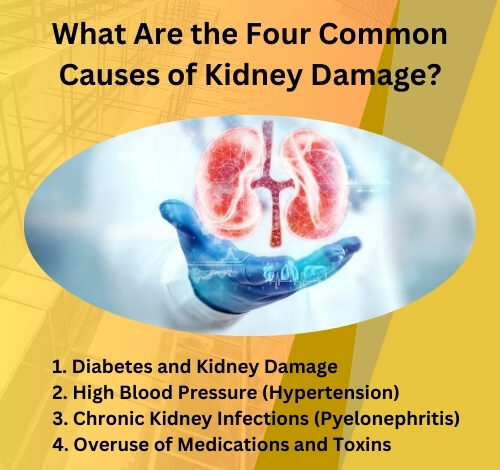
The kidneys are vital organs responsible for filtering waste and excess fluids from the blood, balancing electrolytes, and producing hormones that regulate blood pressure and red blood cell production. However, kidney damage is a prevalent health concern that can lead to chronic kidney disease (CKD) or even kidney failure if left untreated. Understanding the common causes of kidney damage can help individuals take proactive steps to protect their kidney health. The four primary causes of kidney damage: diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic kidney infections, and overuse of medications and toxins.
1. Diabetes and Kidney Damage
How Diabetes Affects the Kidneys
Diabetes is one of the leading causes of kidney damage worldwide. When blood sugar levels are consistently high, the kidneys work harder to filter excess glucose from the blood. Over time, this increased workload can damage the delicate blood vessels in the kidneys, leading to diabetic nephropathy.
Diabetic Nephropathy: A Progressive Condition
Diabetic nephropathy occurs when prolonged high blood sugar levels cause inflammation and scarring in the kidney’s filtering units (nephrons). This condition progresses in stages, starting with increased protein leakage in the urine and eventually leading to kidney failure if left unmanaged.
Risk Factors and Early Symptoms
Certain factors increase the risk of diabetic nephropathy, including:
- Poorly managed blood sugar levels
- High blood pressure
- Genetic predisposition
- Obesity
- Smoking
Early symptoms include:
- Swelling in the legs, feet, or hands
- Increased need to urinate
- High blood pressure
- Fatigue
Prevention and Management
- Maintain optimal blood sugar levels through diet, exercise, and medication.
- Monitor kidney function through regular check-ups.
- Control blood pressure to reduce strain on the kidneys.
- Adopt a kidney-friendly diet low in sodium, protein, and processed foods.
2. High Blood Pressure (Hypertension)
How Hypertension Affects Kidney Function
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is another major contributor to kidney damage. The kidneys rely on a network of blood vessels to function properly. When blood pressure is consistently high, these blood vessels can become narrowed or weakened, reducing blood flow to the kidneys and impairing their ability to filter waste.
The Link Between Hypertension and Kidney Disease
Hypertension and kidney disease often create a vicious cycle: damaged kidneys struggle to regulate blood pressure, leading to further increases in blood pressure, which in turn exacerbates kidney damage.
Warning Signs and Symptoms
- Persistent high blood pressure
- Swelling in the lower extremities
- Changes in urine color or frequency
- Shortness of breath and fatigue
Controlling Blood Pressure to Protect Kidneys
- Reduce sodium intake to prevent fluid retention.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Take prescribed blood pressure medications as directed.
- Manage stress through mindfulness practices.
3. Chronic Kidney Infections (Pyelonephritis)
Understanding Kidney Infections
Chronic kidney infections, also known as pyelonephritis, occur when bacteria travel from the urinary tract to the kidneys. Repeated infections can cause inflammation and scarring, reducing kidney function over time.
How Repeated Infections Damage the Kidneys
Each infection leaves behind scar tissue, which diminishes the kidneys’ ability to filter waste effectively. Chronic kidney infections can eventually lead to kidney failure if untreated.
Signs and Symptoms
- Fever and chills
- Back or side pain
- Frequent urination with a burning sensation
- Cloudy or bloody urine
Prevention and Treatment
- Drink plenty of water to flush out bacteria.
- Practice good hygiene to prevent urinary tract infections.
- Seek prompt treatment for urinary tract infections before they spread to the kidneys.
- Follow prescribed antibiotic courses completely to prevent recurrence.
4. Overuse of Medications and Toxins
Common Medications That Harm Kidneys
Certain medications, particularly when used excessively, can damage the kidneys. Some of the most harmful drugs include:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen and naproxen
- Certain antibiotics like aminoglycosides
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) used for acid reflux
- Some herbal supplements with toxic effects on kidneys
Environmental Toxins and Their Impact
Exposure to heavy metals (like lead and mercury) and industrial chemicals can also contribute to kidney damage. Long-term exposure to toxins may cause kidney inflammation and reduce filtration efficiency.
How to Use Medications Safely
- Take medications only as prescribed by a healthcare professional.
- Avoid long-term use of over-the-counter pain relievers.
- Stay hydrated to support kidney function while taking medications.
- Discuss alternative treatments with your doctor if you have existing kidney concerns.
Detoxifying and Protecting Kidney Function
- Consume a diet rich in antioxidants to combat oxidative stress.
- Reduce alcohol intake and avoid smoking.
- Stay hydrated to flush out toxins naturally.
- Monitor kidney function regularly, especially if taking medications long-term.
Conclusion
Kidney damage is a serious health concern, but understanding its common causes can help individuals take preventive measures. Diabetes, high blood pressure, chronic kidney infections, and overuse of medications or exposure to toxins are four primary contributors to kidney disease. By managing underlying conditions, adopting a healthy lifestyle, and staying informed, individuals can protect their kidneys and maintain overall well-being. Prioritizing kidney health through proactive care can prevent severe complications and improve quality of life.