Histoplasmosis Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis and Treatment
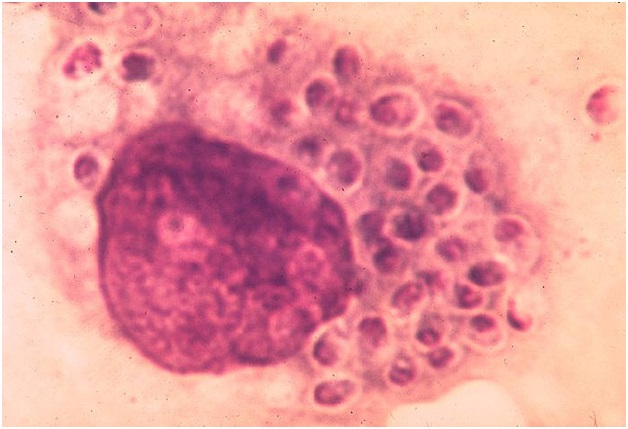
What Is Histoplasmosis ?
Also known as Cave disease, Histoplasmosis is a disease caused by a fungus known as “Histoplama Capsulatum”.
The fungus is naturally found in the environment and may also flourish in bird or bat droppings. If symptoms do occur, Histoplasmosis is known to cause lung diseases similar to those caused by pneumonia.
Histoplasmosis may spread to different parts of the body. If this happens, it is dubbed to be disseminated Histoplasmosis.
Disseminated Histoplasmosis is common in those with weak immune system. The spread is located in the liver, spleen, brain, joints, eyes and bone marrow.
Symptoms, if they occur, start within three to 17 days after exposure and may last for a few weeks. While mild cases do not require ant treatment, severe cases do. In such cases, treatment may involve intake of antifungal drugs.
Causes Of Histoplasmosis :
Histoplasmosis is caused by the spores of the fungus called “Histoplama Capsulatum”. The spores are the reproductive cells of the fungus. They are light and may float in the air upon disturbance to the contaminated material.
When the fungal spores are inhaled, some individuals may develop the infection. Neither is it contagious, nor can it transmitted by person to person contact.
In areas where the fungus is common, between 50%-80% of people will show an antibody response to the organism, meaning that they have been exposed to the fungus at some point in their life.
The infection is more likely to develop in those whose immune system is weakened. Moreover, infants and elderly are at a higher risk of developing it than others.
Symptoms Of Histoplasmosis :
The following symptoms may be exhibited:
- fever
- dry cough
- chest pain
- joint pain
- red bumps on lower legs
- excessive sweating
- shortness of breath
- coughing up blood
- Muscle aches
- Headaches
- Chills
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Confusion
- Seizure
- Vision impairment
Diagnoses Of Histoplasmosis :
Histoplasmosis is diagnosed via:
- Samples containing the fungus taken from sputum, blood or infected organs
- Blood or urine samples, which may detect antigens
- Test for antibodies which work against the fungus
- Histoplasmaskin tests
Treatment Of Histoplasmosis :
No treatment is required for mild cases of Histoplasmosis. However, in case of severe Histoplasmosis, the following treatments are available:
- Antifungal medications
- treatment withamphotericin B, followed by oral itraconazole
By : Natural Health News




